Have you ever wondered how most electronics devices are produced? Or how we can create cost effective disposable electronics? We owe many advances and cost savings to a simple technology called printed circuit boards (PCB) and its various assembly methods.
The electronics industry has undergone a remarkable transformation over the past century, evolving from rudimentary components to sophisticated smart manufacturing processes. From the early days of vacuum tubes and transistors to today’s complex integrated circuits and advanced automation techniques, each phase of development has contributed to the industry’s current state.
The Dawn of Electronics Assembly
Early Innovations and Milestones
The early years of electronics assembly were marked by groundbreaking innovations that laid the foundation for today’s advanced technologies. At the core of these developments were vacuum tubes and transistors. Vacuum tubes, first introduced in the early 20th century, revolutionized the field by enabling the amplification of electrical signals, which was essential for radio and television technology.
The subsequent invention of the transistor in 1947 by Bell Labs marked a pivotal milestone, offering a more compact, efficient, and reliable alternative to vacuum tubes. This breakthrough not only led to the miniaturization of electronic devices but also paved the way for the development of integrated circuits. These early innovations were crucial in transitioning from bulky, power-hungry components to more sophisticated and efficient systems, setting the electronics industry on a path of rapid advancement and modernization.
Early History
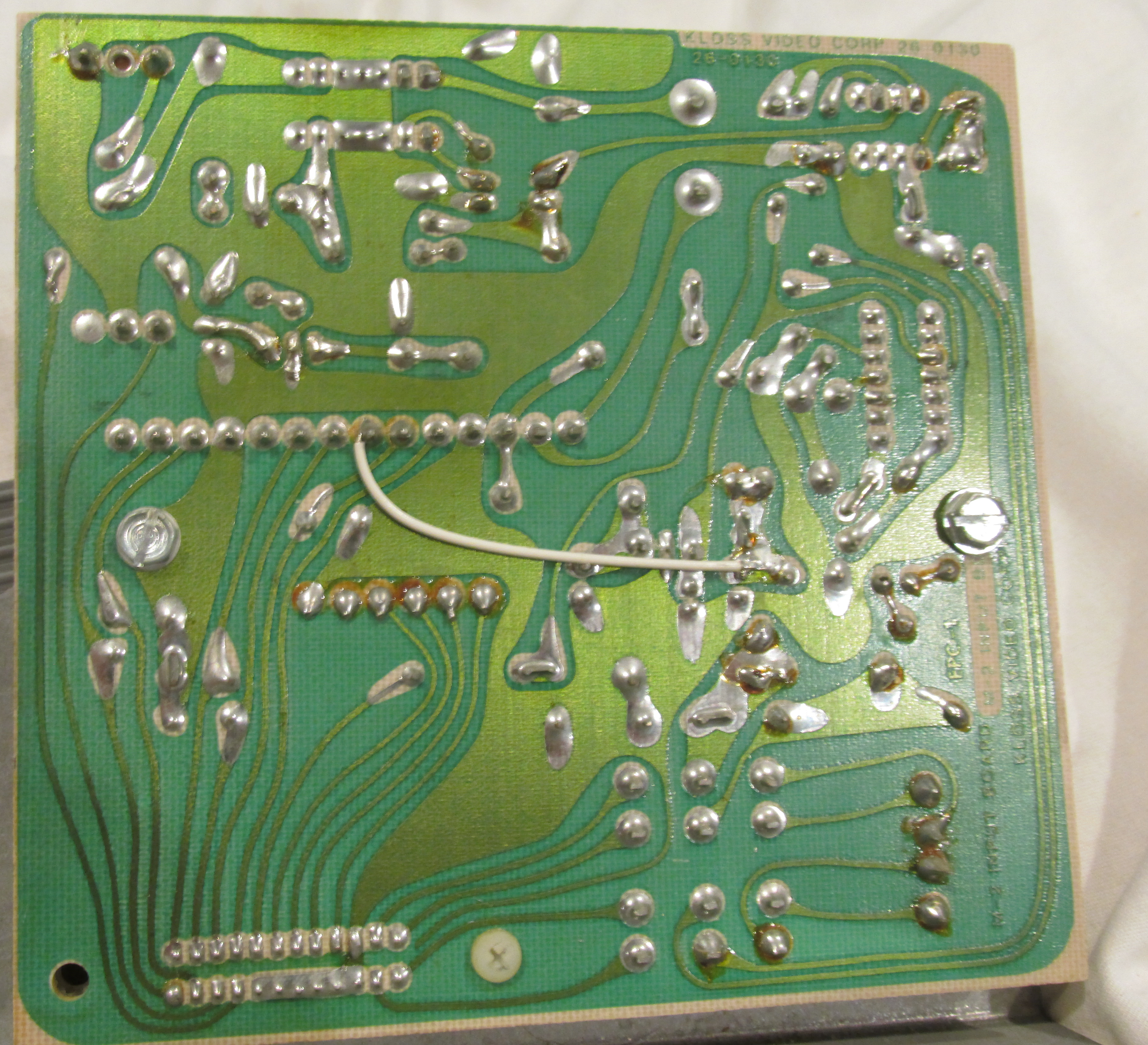
Before circuit boards, electronics were a mess of wires and components! Components and wires would be soldered directly to each other. This is known as point-to-point construction.
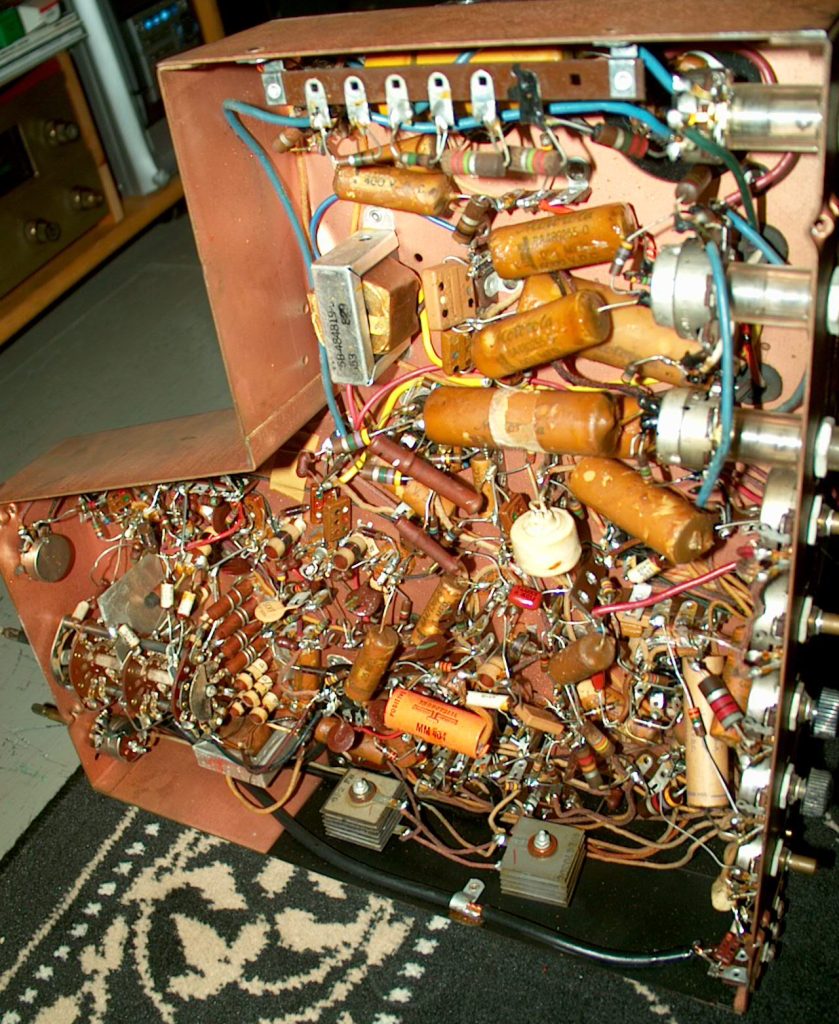

Using the Motorola Goldenview as an example, you can see that manufacturing this would be difficult and would be dependent on skilled people remembering where each point had to be connected to.
Much of this changed with the use of circuit boards, which allowed easier assembly by humans. As time progressed eventually manually assembled circuit boards led to automation of pick and place of components, greatly speeding up the manufacturing process.
Pioneering Manufacturing Techniques
In the nascent stages of the electronics industry, pioneering manufacturing techniques played a critical role in shaping the trajectory of electronics assembly. Manual assembly was the norm, with skilled workers meticulously soldering components onto circuit boards. This method, while labor-intensive, set the stage for more efficient manufacturing processes. The introduction of wave soldering in the 1950s marked a significant advancement, automating the soldering process and increasing production speed and consistency. This technique allowed for greater precision and reliability, essential for mass production.
Additionally, the development of printed circuit boards (PCBs) revolutionized electronics assembly by providing a compact and efficient platform for mounting components. These innovations not only improved manufacturing efficiency but also enhanced the performance and reliability of electronic devices. These early techniques laid the groundwork for the sophisticated, automated processes that characterize smart manufacturing in today’s electronics industry.
Introduction of Circuit Boards
A printed circuit board (PCB) serves to bring together the huge number of resistors, capacitors, logic chips, controllers, etc to function as a single device. Th board helps to support and connect all the components together in a precise repeatable way, forming the circuits needed for the device to function. You can think of it as a road for cars, it serves to connect the points where we want to travel between.
PCBs were first used with manual assembly methods, typically with through hole components and, where human workers would assemble the components by hand onto the PCB and solder the components to create the connection.
Impact on Manufacturing History
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on the manufacturing history of electronics, driving advancements that continue to influence the industry today. This era heralded a shift from handcrafting to mechanized production, introducing machinery that increased both the scale and speed of manufacturing processes. In the electronics sector, this transition facilitated the mass production of components such as resistors, capacitors, and early semiconductors. The ability to produce components on a large scale reduced costs and made electronic devices more accessible to consumers. Moreover, the integration of assembly lines and automation techniques streamlined electronics assembly, enhancing productivity and consistency.
These developments not only accelerated the pace of technological innovation but also laid the groundwork for future advancements in smart manufacturing. By embedding principles of efficiency and scalability into the manufacturing process, the Industrial Revolution set the stage for the modern electronics industry’s ability to rapidly evolve and adapt to new technological challenges.
The Next Leap in Electronics Assembly
PCB technology hand in hand with Surface Mount Technology (SMT) allowed for large scale mass production to take off. Now you have mass produced circuit boards being assembled with components by a pick and place machine capable of over 100,000 components an hour.
Surface Mount Technology has allowed for quick mass production of circuit boards and electronic devices. Standardised components available from less than 1mmx1mm to more than 1cmx1cm can be quickly assembled.
Rise of the Electronics Industry
The rise of the electronics industry during the Industrial Revolution marked a transformative period that reshaped global markets and technological landscapes. As mechanization took hold, the production of electronic components became more efficient, leading to an unprecedented expansion of the industry. This growth was fueled by the increasing demand for consumer goods such as radios, televisions, and, later, computers. Innovations in materials science and engineering further propelled the industry’s evolution, with the development of new semiconductors and electronic devices.
These advancements enabled more complex and efficient electronic systems, laying the groundwork for the digital age. The electronics industry’s expansion also spurred economic growth, creating new jobs and industries. This era established electronics as a cornerstone of modern industrial society, driving continuous innovation and setting a foundation for future technological breakthroughs. The electronics industry’s rise during this period underscores the profound impact of the Industrial Revolution on shaping modern technology and manufacturing practices.
Modern Advances in Smart Manufacturing
Integration of Technology and Innovation
The integration of technology and innovation has become a defining feature of modern advances in smart manufacturing within the electronics industry. This integration is characterized by the adoption of cutting-edge technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics. These technologies have revolutionized electronics assembly by enhancing precision, efficiency, and adaptability. IoT-enabled devices allow for real-time monitoring and data analysis, enabling manufacturers to optimize processes and reduce downtime.
AI applications facilitate predictive maintenance and quality control, ensuring consistent product quality. Robotics have transformed production lines, allowing for automated, high-speed assembly of complex components. This technological synergy not only increases productivity but also supports sustainable manufacturing practices by minimizing waste and energy consumption. By embracing these innovations, the electronics industry continues to lead in smart manufacturing, demonstrating how technology can drive efficiency and innovation in production processes to meet the demands of an ever-evolving market.
Future Trends in Electronics Assembly
The future of electronics assembly is poised for transformative changes driven by emerging trends in smart manufacturing. One significant trend is the increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, which emphasize the digitalization and automation of manufacturing processes. This shift will see greater use of advanced robotics, machine learning, and real-time data analytics to enhance production efficiency and flexibility. Additionally, the rise of additive manufacturing, such as 3D printing, is set to revolutionize the development and customization of electronic components.
This technology allows for rapid prototyping and on-demand production, reducing lead times and material waste. Furthermore, the integration of sustainable practices will become more prevalent, with a focus on minimizing environmental impact through energy-efficient processes and recyclable materials. As consumer demand for smaller, more powerful devices grows, the electronics assembly industry will continue to innovate, leveraging these trends to improve product quality and manufacturing sustainability while meeting evolving market needs.
Get in touch with us to see how we can help you!