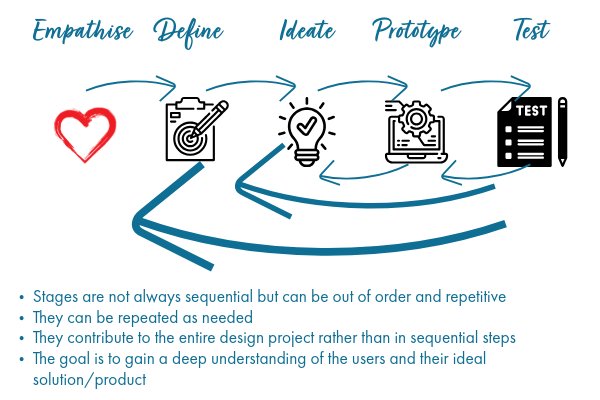
Unleashing Innovation through design thinking is revolutionizing the product design and development landscape, particularly within the medical device, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and allied healthcare industries. This human-centric approach empowers teams to empathize with users, precisely define challenges, ideate innovative solutions, and rigorously prototype and test concepts. By integrating design thinking into the product design and development process, companies can foster creativity, enhance cross-disciplinary collaboration, and ultimately produce impactful products that align with user needs and market demands. In this article, we will delve into the stages of design thinking and illustrate its significant benefits in transforming the product development journey.

Introduction to Design Thinking
Empathizing with Users
Empathizing with users is the foundational stage of the design thinking process. It requires teams to deeply understand the user experience by observing and engaging with individuals to uncover their needs and challenges. In sectors like medical devices and pharmaceuticals, this stage involves comprehensive research, including interviews and field studies, to gain insights into the users’ perspectives. By doing so, teams can identify unmet needs and pain points that may not be immediately obvious. This understanding is crucial as it informs the subsequent stages of the product design and development process, ensuring that the solutions developed are grounded in real-world user contexts. Empathizing with users not only fosters innovation but also builds trust and confidence, as products are tailored to address specific user demands effectively, enhancing the overall impact and acceptance of the final product.
Defining Clear Problems
Defining clear problems is a critical step in the design thinking process. Building on insights gained from empathizing with users, this stage involves synthesizing information to articulate the core issues that need addressing. In medical device and pharmaceutical industries, accurately defining problems ensures that the product design and development efforts focus on genuine user needs and industry challenges. This step often includes creating problem statements that are clear, concise, and centered on the user’s perspective. By narrowing down to specific issues, teams can avoid the pitfalls of vague or broad problem definitions, which can lead to misaligned solutions. This clarity allows for targeted ideation and innovation, directing resources and creativity towards solving the right problems. In essence, defining clear problems lays the groundwork for efficient and effective product development, guiding teams to develop solutions that are both practical and impactful in meeting market demands.
Ideating Innovative Solutions
Ideating innovative solutions is the creative heart of the design thinking process. After clearly defining the problems, teams engage in brainstorming sessions to generate a wide array of potential solutions. This stage encourages unrestricted thinking and the exploration of diverse ideas, fostering an environment where creativity thrives. Techniques such as mind mapping, sketching, and collaborative workshops are commonly employed to stimulate ideation. In the context of medical device and pharmaceutical industries, this phase is particularly crucial as it can lead to breakthroughs that significantly improve patient outcomes and user experiences. The goal here is to think beyond conventional approaches and consider novel solutions that address the defined problems effectively. By embracing a multitude of perspectives, teams can uncover innovative pathways that might have been overlooked in a more traditional product design and development process. Ultimately, ideating innovative solutions sets the stage for developing prototypes that can be tested and refined, ensuring that the best ideas move forward.
Prototyping Concepts
Prototyping concepts is a pivotal phase in the design thinking process, where ideas transition from abstract to tangible. This stage involves creating simple and cost-effective models of proposed solutions, allowing teams to explore their viability and functionality. In industries such as medical devices and pharmaceuticals, prototyping can range from digital simulations to physical models, depending on the nature of the product. The objective is to build prototypes that can be easily modified based on feedback, facilitating rapid iteration. Prototyping provides a low-risk platform for testing hypotheses and refining concepts, ensuring that only the most promising ideas proceed to the development stages. This hands-on approach helps identify potential design flaws early, allowing for adjustments that enhance the final product’s effectiveness and user satisfaction. By integrating prototyping into the product design and development process, companies can minimize risks, reduce costs, and accelerate time-to-market, ultimately delivering solutions that are well-aligned with user needs and expectations.
Testing and Iteration
Testing and iteration are crucial elements of the design thinking process that ensure a product meets user needs and expectations. At this stage, prototypes are tested in real-world scenarios to gather valuable feedback from users and stakeholders. This feedback is essential for identifying any shortcomings or potential improvements. In sectors like medical devices and pharmaceuticals, rigorous testing is vital to ensure safety, efficacy, and regulatory compliance. The process is iterative, meaning that testing often leads back to ideation and prototyping, allowing teams to refine and enhance the product continuously. By embracing an iterative approach, companies can adapt to changing requirements and insights, ensuring that the final product is both innovative and effective. This cycle of testing and iteration helps mitigate risks, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately produce solutions that are robust and market-ready. Integrating this approach into the product design and development process fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, aligning closely with user and market demands.